Which Process in Eukaryotic Cells Will Normally Proceed Whether O2 Is Present or Absent?
1
Metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules
2
Pinocytosis or Receptor-mediator
Endocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell.
3
ATP made during glycolysis is generated by what?
Substrate-level phosphorylation
4
Oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
Accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
5
During cellular respiration, acetyl CoA accumulates in which location?
6
The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in a redox or oxidation-reduction reaction...
Loses electrons and loses potential energy
7
When a molecule of NAD+ gains a hydrogen atom, not a proton, the molecule becomes _____.
8
Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O2) is present or absent?
9
During glycolysis, when each molecule of glucose is catabolized to two molecules of pyruvate, most of the potential energy contained in glucose is...
Retained in the two pyruvate
10
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) is released during which of the stages of cellular respiration?
Oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and the Citric Acid Cycle
11
The proteins of the electron transport chain are located where
Mitochondrial Inner Membrane
12
In cellular respiration, the energy for most ATP synthesis is supplied by...
A proton gradient across a membrane
13
Primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to...
Act as an acceptor for electron and hydrogen, forming water
14
Inside an active mitochondrion, most electrons follows which pathway?
Citric Acid Cycle -> NADH-> Electron Transport Chain -> Oxygen
15
In chemiosmosis, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP + i to ATP?
Energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase, down their electrochemical gradient
16
Energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ into which location in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondrial Intermembrane Space
17
ATP synthase is located where in the mitochondrion?
18
The force provided by a transmembrane hydrogen ion gradient
19
Along with glycolysis, where does fermentation take place in eukaryotic cell?
20
Without oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of...
ATP, CO2, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
21
The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that functions in aerobic oxidative phosphorylation is ____.
22
Formation of acetyl CoA takes place in the _____.
23
The citric Acid Cycle Takes place in the ______.
24
Oxidative Phosphorylation occurs where?
Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
25
Name the net input for oxidative phosporylation
26
Name the net output for oxidative phosporylation
27
Net input involved in Citric acid Cycle
28
Net output involved in citric acid cycle
29
Pyruvate, NAD+, coenzyme A are my inputs
Acetyl CoA, NADH, CO2 are my outputs
who am I
30
My net inputs are ADP glucose, and NAD+
My net outputs are ATP, NADH, and pyruvate
what am I
31
The reactions of cellular respiration can be broken down into four stages...
1. Glycolysis
2. Acetyl CoA (Coenzyme A)
3. Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
4. Oxidative Phosphorylation
32
When a compound donates (loses) electrons, that compound becomes _______. Such compound is often referred to as an electron donor.
33
In glycolysis, the carbon-containing compound that functions as the electron donor is _______.
34
Once the electron donor is glycolysis gives up its electrons, it is oxidized to a compound called...
35
_____ is the electron acceptor in glycolysis
36
Reduced form of electron acceptor in glycolysis is _______
37
What compounds in glycolysis which compounds can be used in other biological reactions?
38
In lactate, what is the product of pyruvate metabolism?
Fermentation in human muscle
39
In ethanol what is the product of pyruvate metabolism?
Fermentation in yeast and bacteria
40
Main purpose of combined processes of glycolysis and cellular respiration
Transformation of the energy in glucose and related molecules in a chemical form that cells can use for work
41
Electrons shipped from glucose in cellular respiration end up in which compound?
42
What results from an unequal sharing of electrons betweens atoms?
43
A covalent bond is likely to be polar when
One of the atoms sharing electrons is much more electronegative than the other atom
44
What charge does a proton have?
45
What charge does a neutron have?
46
What charge does an electron have?
47
Which subatomic particles both have masses of about 1 amu?
48
What determines the types of chemical reactions that an atom participates in?
The number of electrons in the outermost electron shell
49
What type of bond is one in which electron pairs are shared?
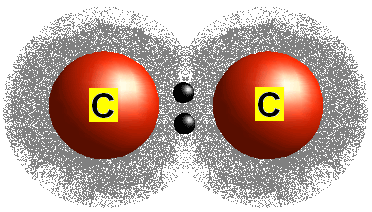
Covalent Bond
50
______ refers to two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
51
An ionic bond involves an attraction between ions of
52
Atoms with the same number of protons but with different electrical charges are _______
53
In salt, what is the nature of the bond between sodium and chloride
54
The type of bonding and the numbers of covalent bonds an atoms can form with other atoms is determined by _____
The number of unpaired electrons in the valence shell
55
What type of bond do atoms with similar electronegativities have?
56
What bond is formed when one atom transfers an electron to another atom?
57
Hydrogen bonding is most often seen when hydrogen is...
covalently bonded to an electronegative atom
58
Tendency of dissimilar particles/ surfaces to cling to one another
59
The attraction between like molecules (water forms drops on table)
60
Resistance of the surface of a liquid of stretching or breaking
61
Resists change is pH by accepting hydrogen ions when acids are added to the solution and donating hydrogen ions when bases are added
62
Buffers minimize the change in the ____ of a solution
63
What forms when two atoms transfer or share outer electrons to complete their outer shells?
64
Most organic compounds contain which two elements?
65
Large diversity of shapes of biological molecules is possible because of the extensive presence of ______ in the molecule.
66
Chemical energy is a form of _____ energy
67
Process that converts chemical energy found in glucose into chemical energy found in ATP.
68
What are 3 by-products of cellular respiration?
Heat, carbon dioxide, and water
69
In a cell, what is usually the immediate source for an endergonic reaction?
70
A reaction in which the net input of energy is required from its surroundings
71
In an endergonic reaction, the _______ have more potential energy than the ______.
72
In an exergonic reaction the ______ have less potential energy than the _______.
73
ADP + P --> ATP is a....
74
The energy released by an exergonic reaction can be used to...
drive an endergonic reaction
75
What is the fate of the phosphate group that is removed when ATP is converted to ADP?
It is acquired by a reactant in an endergonic reaction
76
The use of energy released form an exergonic reaction to drive an endergonic reaction
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed but can be converted from one form to another
78
What reaction breaks the bonds that join the phosphate group in an ATP molecule?
Building of complex molecules from simple ones
80
Energy needed or produced from a catabolic or anabolic process is stored where?
Intermediate energy carrying molecules such as ATP
81
A catabolic/ anabolic process requires energy.
82
A catabolic/ anabolic process generates energy.
83
In general, enzymes are what kind of molecules?
By reducing the energy of activation
85
Enzymes are proteins that behave as...
86
After involvement in an reaction, an enzymes results are changed.
87
For a reaction to proceed, ________ must be overcome.
88
The name given to a reactant in an enzymatically catalyzed reaction.
89
Generally, how many active sites at which catalysis can occur in an enzyme?
90
The movement of glucose into a cell against a concentration gradient is most likely to be accomplished by...
Co-transport of the glucose with a proton or sodium ion that was pumped across the membrane using the energy of ATP hydrolysis
91
What type of molecules are the major structural components of the cell membrane?
Phospholipids and proteins
92
Singer and Nicolson's fluid mosaic model of the membrane produced that membranes...
Consist of protein molecules embedded in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids
93
The presence of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of some animals
enables the membrane to stay fluid more easily when cell temperature drops
94
The primary function of polysaccharides attached to the glyclo-proteins and glycolipids and animal cell membranes is...
To mediate cell-to-cell recognition
95
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily?
96
True/ False
Diffusion is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
97
Pinocytosis/ Receptor-mediator Endocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell.
98
Pinocytosis/ Receptor-mediator Endocytosis offers more selectivity in the cells it brings into the cells
Receptor-mediator Endocytosis
99
A bacterium engulfed by a white blood cell through phagocytosis will be digested by enzymes contained in...
100
Substance that acts at a long distance from the site at which it is secreted.
101
Advantage of light microscopy over electron microscopy is that...
Light microscopy allows one to views dynamic processes in living cells
102
____ are surfaces appendages that allow a bacterium to stick to a surface
103
What is the function of a bacterium's capsule?
104
Where is a bacterial cell's DNA found?
105
In bacterium where are proteins synthesized?
106
The rigid structure, found outside the plasma membrane, that surrounds and supports the bacterial cell?
107
The bacterial structure that acts as a selective barrier, allowing nutrients to enter the cell and wastes to leave the cell
108
What clue tells if a cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Whether or not the cell is partitioned by internal membranes
109
What are the two domains of prokaryotes?
110
What is the first of the two main steps of proteins synthesis?
111
Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing what molecule?
112
Which structure is the site of the synthesis of proteins that may be exported from the cell?
113
Which polymers are composed of amino acids?
114
Which monomers make up RNA?
115
What happens between the formation of polypeptides from amino acids?
a bond forms between the carboxyl functional group of one amino acid and the amino functional group of the other amino acid
116
Which molecule is not a carbohydrate?
cellulose, glycogen, lipid, starch
117
What is the function of cellulose?
It is the structural component of plant cell walls
A polysaccharide found in animals
119
_______ is the most abundant organic compound on Earth
120
Lactose, the sugar in milk, is a _____ because it can be split into two monosaccharides
121
Phospholipids are composed of a ____, ____, and a ____.
Phosphate group, a glycerol, and fatty acids
122
The sequence of amino acids in a protein
123
The pattern of hydrogen bonds of the protein, such as alpha-helices and beta sheets, that are observed in an atomic resolution structure
124
Achieved when a protein folds into a compact, three-dimensional shape, stabilized by interactions between side chain "R-groups" of amino acids
125
The result of two or more protein subunits assembling to form a larger, biologically active protein complex
126
Two strands of a DNA double helix are held together by _____ that form between pairs of nitrogenous bases
127
Which linkage forms the backbone of a nucleic acid?
128
List the levels of biological organization from the most wide to the most specific
1. Biosphere
2. Ecosystems
3. Communities
4. Populations
5. Organisms
6. Organs and Organ Systems
7. Tissues
8. Cells
9. Organelles
10. Molecules
129
Approach of reducing complex systems to simpler components that are more manageable to study
130
5 themes that help organize biological information and help understand life better.
1. Organization
2. Information
3. Energy
4. Interaction/ communication
5. Evolution
131
Descent with modification; the idea that living species are descendants if ancestral species that were different from the present-day ones; the change in the genetic composition of a population from generation to generation
132
New properties arise with each step upward in the hierarchy of life, owing to the arrangement and interactions of parts as complexity increases.
133
A cell with a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles
134
Eukaryotic/ Prokaryotic cells
protists, plants, fungi, and animals
135
A cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles
136
Eukaryotic/ Prokaryotic cells
bacteria and archaea
137
Discrete unit of hereditary information consisting of a specific nucleotide sequence in DNA or RNA
138
Process by which information encoded in DNA directs the synthesis of proteins or, in some cases, RNAs that are not translated into proteins and instead function as RNAs
139
Genetic material of an organism of virus; the complete complement of an organisms genes along with its nucleic acid sequences
140
Name the three domains
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya
141
Which two of the three domains are prokaryotic?
142
What domain includes three kingdoms of multicellular eukaryotes, what are the three kingdoms?
Eukarya; Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia
143
Mostly unicellular eukaryotes and some relatively simple multicellular relatives
144
What kingdom consists of terrestrial multicellular eukaryotes (land plants) that carry outs photosynthesis, the conversion of light energy to the chemical energy in food
145
Which kingdom is defined in part by the nutritional mode of its members (such as this mushroom) which absorb nutrients from outside their bodies
146
Explain natural selection
Process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits
147
Search for information, often focusing on specific questions
148
Type of logic in which generalizations are based on a large number of specific observations
149
True/ False
A hypothesis is narrower in scope than a theory
150
Type of logic in which specific results are predicted from a general premise
151
An experiment in which an experimental group is compared with a control that varies only in the factor being tested
152
Explanation that is broader in scope than a hypothesis, generates new hypothesis and is supported by a large body of evidence
153
All the organisms in a given area as will as the abiotic factors with which they interact; one or more communities and the physical environment around them
154
A group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area and interbreed, producing fertile offpring
155
All the organisms that inhabit a particular area; an assemblage of populations of different species living close enough together for potential interaction
156
An organisms basic unit unit of structure and function
157
Qualitative data is information with the use of...
Descriptions rather than measurements
158
Quantitative data is information with the use of...
Recorded measurements which are sometimes organized into tables and graphs
Which Process in Eukaryotic Cells Will Normally Proceed Whether O2 Is Present or Absent?
Source: https://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/37612
0 Response to "Which Process in Eukaryotic Cells Will Normally Proceed Whether O2 Is Present or Absent?"
Post a Comment